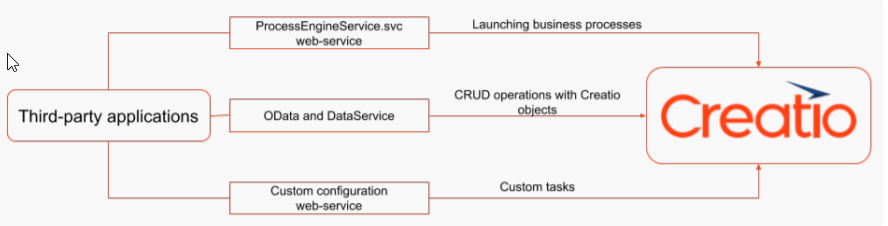
What is SaaS (Software as a service)?
SaaS meaning
Software as a service (SaaS) is cloud-based software, which means you can access it through an internet browser and do not have to install an application on your device.
A survey by Finances Online states that 86% of companies will be running on SaaS by 2023. According to Deloitte, 70% of CIOs are attracted to cloud-based SaaS because of its agility and scalability, and 38% of companies choose to adopt cloud-based systems to enhance disaster recovery.
Today it doesn’t come as surprise that adopting SaaS should be considered by every company looking to strengthen its resilience, adaptiveness and accelerate growth.
Let’s dive deeper into the SaaS functionality, benefits and main characteristics, and see why it’s trending now.
How does software as a service work?
Traditional software is installed on computers and requires an admin to maintain and update. When a program is available via the website or application, it is called Software as a Service (SaaS).
Software as a Service is located on a hosted platform, eliminating the hardware and software maintenance-related issues. Updates are usually done on the service provider’s side. Thus, SaaS saves time and money on software deployment, cuts down operating costs, and reduces risks and vulnerabilities.
Advantages of SaaS
1 Accelerated deployment
For midsize and large enterprises, software implementation projects might take months or years. With SaaS the deployment time reduces significantly as purchase and configuration of hardware is taken out of the scope of works. Vendors provide access to their services in the cloud and users right away gain access to advanced tools to automate business processes, streamline workflows, and accelerate operations.
2 Accessibility
SaaS applications are usually accessed through a web browser. Because it’s a subscription-based service, organizations can easily scale up or cut down on the number of licenses provided to end users at any point. SaaS apps are compatible with any operating system, including macOS, Windows, and Linux, as well as Android and iOS. Mobile accessibility enables users to take full advantage of SaaS features on the go using tablets and smartphones.
3 Customization and integration
SaaS services enable deep customization so apps can be configured specifically to each customer’s requirements, including the functionality and look-and-feel of the product. Such systems can also be integrated with other business apps, especially across applications from a common software provider.
4 Data and analytics
With a SaaS application, all processes, data and files are carried out through a centralized platform, making it easy to collect, store and analyze data further, even for distributed teams. Organizations using SaaS gain secure company-wide access to the information and tools that provide insights into business operations and customer data, enabling them to ensure high engagement for employees and customers, and improve processes.
5 Saving and storage
With SaaS, data is always saved in the cloud allowing users to securely store their data, get additional storage space when needed, and switch between devices without losing access.
Some SaaS vendors provide the ability to install SaaS on-premise. This provides companies more control over their data and access to it. However, this way of installation requires extra IT support and increases maintenance costs. It may also lead to a risk of data loss due to a malfunction in the system or a compromised system held for ransom. In order to avoid such issues, a company must have an in-house team for maintenance.
6 Updates and patches
Since SaaS applications run in the cloud, providers can update their software centrally without affecting business operations for users or relying on in-house IT teams to timely upgrade to new versions.
The SaaS model helps to avoid testing errors that slow down the development cycle and as a result, provides users with timelier access to new features. At the same time, it ensures that security updates are applied as soon as possible. On the other hand, on-premises software remains vulnerable to attacks until the IT department management staff prioritizes their backlog, installs patches and runs test.

Try Creatio SaaS intelligent products
Disadvantages of SaaS
1 Switching vendors
When switching vendors, customers have to transfer large amounts of data. In addition, some vendors use proprietary technologies and data types, making it even more difficult to transfer data between cloud providers. A situation where a customer cannot easily switch between service providers is called “vendor lock-in.” To address the issue, SaaS solution providers release connectors that enable smooth migration from legacy to new software.
2 Losing control over versioning
In case a provider releases a new version of the application, it will apply to all clients, regardless of whether the customer wants the new version or not. Thus, the company might have to spend time and resources on training. However, enterprise applications tend to be more and more intuitive and user-friendly today, eliminating the steep learning curve for end users.
3 Issues on the vendor’s side
Service disruptions, changes in service offerings, security breaches — all these issues can affect a customer's ability to use SaaS. To avoid these problems, customers need to be familiar with the terms and conditions of their SaaS provider.

SaaS Characteristics
Software as a Service (SaaS) applications have a robust range of features and characteristics, but some of the key ones are the following:
-
Configuration and customization
SaaS applications allow users to configure them, meaning that a customer can alter the set of configuration parameters that affect SaaS functionality. The application can be customized by a customer to the degree it was designed for based on predefined options.
-
Low-code/No-code technology
More advanced SaaS applications provide users with low-code and no-code technologies that allow traditional developers and citizen developers to rapidly build, adjust, customize, and re-configure applications, as well as integrate them into existing IT enterprise landscape. A low-code app development approach requires very little knowledge of basic developing skills, while no-code tools don’t require coding skills at all.
-
Multitenant architecture
Multitenancy is a type of software architecture where a single deployment of an application serves multiple customers. Each customer is called a tenant.
-
Accelerated feature delivery
SaaS applications are updated more frequently than traditional software, sometimes on a weekly or monthly basis. Accelerated feature delivery is enabled because the application is hosted centrally, has a single configuration, and the application vendor has access to all customer data, expediting design and regression testing.
-
Open integration protocols
SaaS application cannot access a company’s internal systems (databases), this is why they usually offer integration protocols and APIs (application programming interfaces).
-
Single sign-on
SaaS applications allow enterprises to have a single identity system in order to authenticate various systems that will be utilized by users.
Software as a Service applications can be easily integrated with various identity management systems. -
Subscription-based billing
SaaS applications are subscription-based enabling customers to purchase licenses whenever needed or terminate the subscription if the solution no longer satisfies business needs. Subscription types usually depend on the number of active users and required features. Companies purchasing a software may be billed monthly/quarterly/ semiannually/annually, etc.
SaaS
On-premise
Fee payment is required on a recurring basis. Most SaaS companies offer a free trial to all users before a fee is applied
A one-time fee is required where the buyer pays a fixed amount upfront
Doesn’t require to install anything on your computer or laptop, as the software runs on a cloud server
Runs on a computer or laptop and requires the software to be installed before the application can begin functioning
Offers automatic software updates that don’t require action from the user’s side
Frequent updates are required with on-premise software and must be managed by the buyer
Can be used by multiple users simultaneously
Can be used by a single or a couple of users
Offers better security, and there is no need for data backups
Relies on the protection of your system's antivirus or firewalls and requires regular backups of the important data
Takes care of the maintenance costs of running the software, which cuts down expenses
Requires a piece of software for every computer, with extra maintenance costs
Can be accessed from any desktop computer, laptop, tablet or mobile phone
Can be used only on a single device on which the software is installed
So which option is better?
Buyers don’t have to choose between agility and functionality anymore. Today most cloud-based software can offer the same experience as with an on-premise installation.
With a robust set of capabilities, tools for customization and multiple subscription options, SaaS apps help organizations from various industries implement reliable and modern software. SaaS applications make it possible to perform business operations while on-the-go, anytime, from any device connected to the Internet. Today, when the hybrid work environment prevails and anywhere operations are one of the trends that organizations can’t ignore, SaaS is a must for any company looking to accelerate its processes and business growth.
FAQ
Who owns the data in SaaS? Is my data safe?
Who owns the data in SaaS? Is my data safe?
Service level agreements confirm your company’s ownership of your data located on the vendor’s servers, as well as your right to retrieve the data.
Most SaaS vendors will let you export your data and back it up locally any time you need.
What are examples of SaaS vendors?
What are examples of SaaS vendors?
Creatio, Microsoft, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Oracle.
Can I customize SaaS software?
Can I customize SaaS software?
Yes. Modern SaaS applications can be modified for specific business uses and individual users. You can customize the user interface to change the look and feel of the program and modify specific areas, such as data fields. SaaS vendors that provide low-code/no-code capabilities, allow users to customize and even create new applications within the solution.
What determines the price of a Saas software?
What determines the price of a Saas software?
Free, or ad-based pricing model provides a free service for users, but the SaaS provider generates revenue by selling advertisement space. In this model, there is usually an option to upgrade to a paid tier that doesn't include ads.
Per user pricing model is determined by how many people will be using the service for each subscription. There is a fixed price for every user.
Storage tiers allow customers to have free access to a service, but they will have to pay for storage in case they want to continue using the product after they pass the free limit.
Feature-based tiers are determined by the scope of features the subscriber needs. Reduced versions of the software with limited features are available for a lower price.